Most AI models currently deployed are based on Machine Learning techniques and help discover and analyse information to make recommendations (ecommerce, Netflix etc), support decision making (healthcare, level 1-3 semi-autonomous driving) and help facilitate and maintain customer interactions (chatbots, robo-advisors). As Deep Learning capabilities improve and are commercialised, the level of sophistication and automation of AI-based systems will increase exponentially.
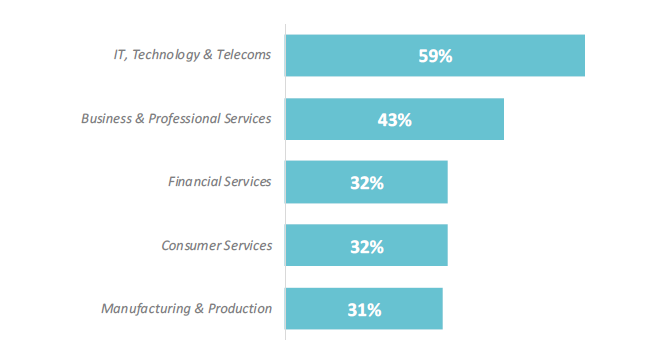
In terms of industries, IT, Business, Professional, Consumer, Financial services and Manufacturingare the super-sectors that stand to benefit the most from AI.
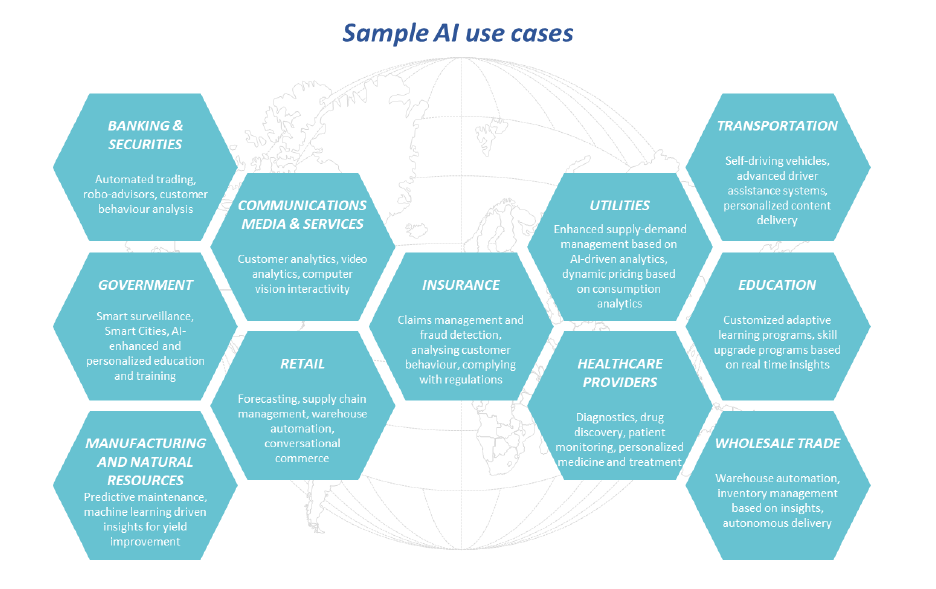
Below we have summarised the main use cases for AI across different sectors & industries. The common threat is that AI aims to add a layer of ‘intelligent’ automation to tasks that are currently done largely by humans. We also highlight that rather than replacing humans, AI systems will often be able to free up time for existing human workers to focus on more ‘value-added’ activities.
Robotics is a good example for an AI system that will require the full suite of AI capabilities across different disciplines in order to maximise its productivity benefits. These are:
- Computer vision and speech recognition for sensing the environment;
- Natural language processing, information retrieval, and reasoning under uncertainty for processing instructions and predicting consequences of potential actions;
- Cognitive modelling and affective computing for interacting and working together with humans.